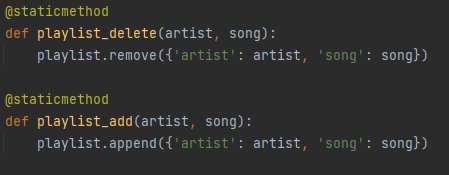
Spotify user credentials
-
The user credentials are supposed to be that of the spotify user playing the music, example is the bar owners spotify account. The scope is what determines which actions are authorized, like putting a song in queue or reading the contents of their playlists.
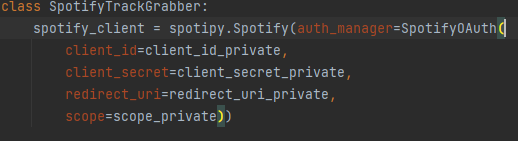
-
In a seperate file, the client information is at the moment hardcoded, but it is supposed to be acquired via the local network in the bar.
-
Here the class TrackGrabber is introduced and it contains methods directly used within in the Spotify API to get the specified information.
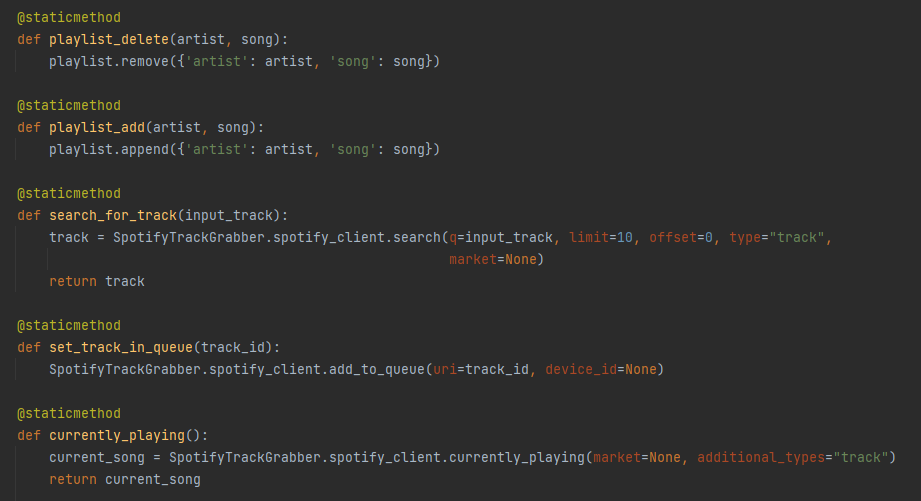
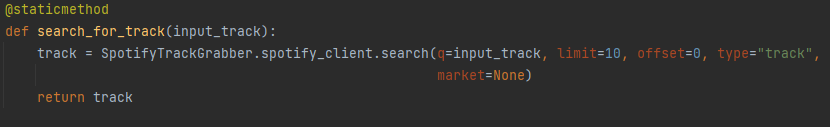
Search for a track.
- One of the most important methods for this project is the ability to search for a track.
- The method has several important parameters that are required. ‘q’ is the input string acquired from the app, example: ‘Kim Larsen - Midt om natten’.
- ‘limit’ is the maximum amount of songs it will return.
- ‘offset’ is where the indexing will start.
- ‘type’ is the type of information returned, in this case it is a track.
- ‘market’ is which market it will choose from.
The internal playlist of the RaspberryPi.
- The RaspberryPi handles the queued songs as a playlist and has an internal variable set as a list with dictionaries inside it, each dictionary is a seperate song containing the name of the artist and the song.

Methods to control the playlist.
- The next two methods within the TrackGrabber class directly works with the internal playlist variable and either removes or appends a song. These methods do not directly use the Spotify API, however they use the data that is acquired when the app is being used.